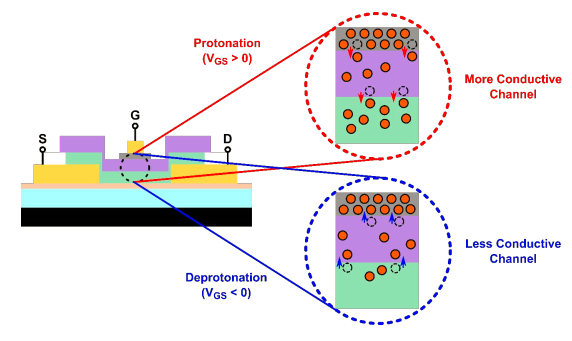
基于离子插层的可编程电阻已成为模拟深度学习应用的潜在下一代技术。质子,作为最小的离子,是一个非常有前途的候选者,可以使器件具有高调制速度、低能耗和增强的耐久性。
美国麻省理工学院-IBM Watson人工智能实验室李巨教授团队发表在NANO LETTER的一篇题目为“基于磷硅酸盐玻璃电解质的CMOS兼容质子可编程电阻用于模拟深度学习”的文章(https://pubs.acs.org/doi/full/10.1021/acs.nanolett.1c01614),报告了第一个后端CMOS兼容的非易失性质子可编程电阻,该电阻通过整合磷硅酸盐玻璃(PSG)作为质子固体电解质层而实现。PSG是一种出色的固体电解质材料,它同时显示出优异的质子传导和电子绝缘特性。此外,它是传统硅制造中的一种知名材料,能够实现精确的沉积控制和可扩展性。规模化的全固态三端设备在对称性、保持性、持久性和能源效率方面显示出理想的调制特性。因此,基于磷硅酸盐玻璃的质子可编程电阻代表了实现单片CMOS集成的纳米级模拟交叉棒处理器的有希望的候选者。
这篇开创性的研究论文中关于CMOS兼容质子可编程电阻的电学表征工作均基于韩国NEXTRON公司变温微探针系统MPS-PT通过和美国Keysight公司的B1500半导体参数分析仪连用进行测试(All electrical measurements were performed using a micro-probe station enclosed chamber (MPS-PT) manufactured by NEXTRON, Korea. In experiments performed in forming gas(FG, 3% H2 in N2) all 4 DC probes where first connected to the pads of the device under test(1 to Source, 1 to Drain and 2 to Gate terminals). The chamber was then purged by flowing in FG for 60 s with both gas inlet and outlet open, followed by another 60 s with outlet shut to create positive pressure inside the chamber.
Three of the probes (1 Source, 1 Drain and 1st Gate) were then connected to the Source Measurement Units (SMUs) of a Keysight B1500 Semiconductor Analyzer, while the fourth probe (2nd Gate) was connected to the Pulse Generation Unit (PGU) of the same instrument. The experiment sequence and data acquisition were controlled via an in-house developed MATLAB suite.)